Vitamin B12 is essential for our body's well-being. Many might not realize how crucial it really is. It plays a significant role in various bodily functions, like the production of red blood cells and maintaining nerve health.
A deficiency in this important vitamin can have serious consequences, leading to fatigue, neurological issues, and more. Understanding the impact of Vitamin B12 deficiency is vital for your overall health.

What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin found in many animal products including meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. It is important for several bodily functions:
- Red Blood Cell Formation: Helps prevent anemia.
- Nerve Health: Supports the nervous system.
- DNA Synthesis: Crucial for cell division.
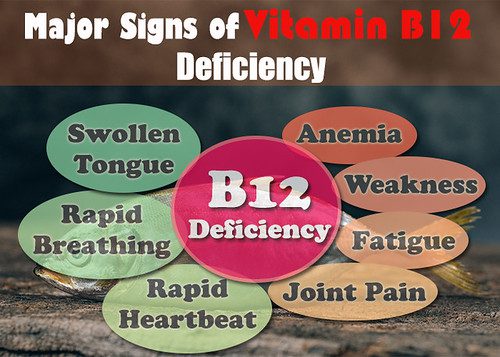
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
A Vitamin B12 deficiency can manifest in various ways. Here are some common signs:
- Extreme Fatigue: Overwhelming tiredness that affects daily activities.
- Neurological Issues: Symptoms might include tingling in hands and feet, confusion, and difficulty walking.
- Mood Changes: Depression and mood swings may occur.
These symptoms can often be overlooked since they mimic other health issues.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Several factors contribute to a Vitamin B12 deficiency:
- Dietary Insufficiency: Vegetarians and vegans may lack sources of this vitamin.
- Absorption Issues: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn's can hinder absorption.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs affect the body's ability to use B12.
Understanding these causes is the first step towards prevention.
The Absorption Process of Vitamin B12
The body absorbs Vitamin B12 through a multi-step process:
- Ingestion: B12 in food combines with saliva's R-protein.
- Stomach Action: Stomach acids and intrinsic factor promote absorption.
- Intestinal Absorption: In the small intestine, B12 enters the bloodstream.
If any step fails, it can lead to a deficiency.
Impact of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Health
A deficiency can lead to serious health issues:
- Anemia: Without enough B12, the body can't produce healthy red blood cells, leading to anemia.
- Nerve Damage: Lack of B12 can lead to nerve damage, which may cause long-lasting issues.
- Cognitive Decline: Some studies link B12 deficiency to memory problems and cognitive decline.
Addressing a deficiency early can reverse these effects.
Treatment for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Treatment options vary depending on the cause:
- Dietary Changes: Incorporate more B12-rich foods.
- Supplements: Oral supplements or injections may be necessary for severe cases.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitoring vitamin levels through blood tests can help prevent deficiencies.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for proper treatment.
Risk Factors for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Identifying risk factors can prevent deficiencies:
- Age: Older adults are at higher risk due to absorption issues.
- Diet: Those on vegan or vegetarian diets might not get enough B12.
- Medical Conditions: Disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract can hinder absorption.
Awareness of these factors can help you take proactive steps.
Healthy Food Sources of Vitamin B12
Include these foods in your diet for adequate Vitamin B12:
| Food | B12 Content |
|---|---|
| Beef | High |
| Clams | Very High |
| Salmon | High |
| Fortified Cereals | Can vary, check labels |
| Milk and Yogurt | Good source |
Vitamins and Supplements to Consider
Consider these essential supplements for health:
| Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Biovanish Weight Loss | Aids in weight management |
| Prosta Dine Prostate Health | Supports prostate function |
| Sightcare Eye Supplement | Promotes eye health |
| NeuroRise Hearing Health | Supports auditory function |
Pros and Cons of Supplements
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Boosts immune function | May cause side effects |
| Supports various health functions | Not a substitute for diet |
| Convenient source of nutrients | Quality varies by brand |
| Can prevent deficiencies | Some may be unnecessary |
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the main symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Symptoms include extreme fatigue, neurological issues, and mood changes.
Who is most at risk for Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Older adults, vegetarians, and those with absorption issues are most at risk.
How can I treat Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Treatment options include dietary changes, supplements, and regular health check-ups.
Can I get enough Vitamin B12 from my diet alone?
Yes, if you consume enough animal products. However, supplements may be needed for those on a restrictive diet.
Is a Vitamin B12 deficiency serious?
Yes, it can lead to long-term health issues if not addressed promptly.
Addressing Vitamin B12 deficiency is crucial for maintaining overall health. Understanding its significance and recognizing its symptoms can make a significant difference in well-being.
Lamartine is an experienced researcher who produces evidence-based content focusing on health, wellness, supplements, lifestyle, and utilities. On the website holistichealthpathways.com, he offers objective, research-backed information to help readers make informed choices.